"Platform Switch" To Preserve Crestal Bone-A new concept in Dental Impant

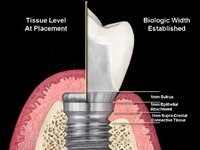
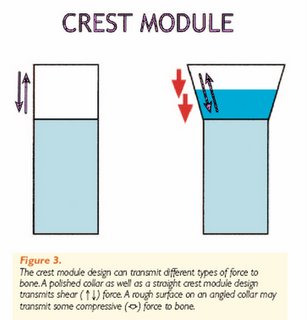 Implant neck (crest module) :The highest bone stresses have been reported to be concentrated in the cortical bone in the region of the implant neck as demonstrated in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of loaded implants with or without superstructure. This is consistent with findings from experimentsand clinical studies that demonstrated that bone loss begins around the implant neck. It has been suggested that the implant neck should be smooth/ polished, supporting the belief that the crest module should not be designed for load bearing. However, significant loss of crestal bone has been reported for implants with 3 mm long smooth polished necks. Following the placement of an endosseous implant,there is an initial bone modeling/ remodeling during healingand the establishment of a biological seal around the neck of the implant. This bone modeling for biologic seal is acombination of a 1.0-1.5 mm junctional epithelium and a 1.5-2.0 mm connective tissue region that is established superior to the alveolar crest. Evidence from in vivo studies supports the observation of establishment of a biologic seal. Hammerle et al did not observe crestal bone to be maintained above the junction of the Titanium Plasma-sprayed Surface (TPS) and machined neck with ITI implant system,and they concluded that polished implant collars do not integrate, as Buser et al demonstrated in his mini-pigmodel. Similarly, bone modeling occurs to the level where the porous surface begins, with the Endopore implants. Disuse atrophy, due to sub-normal mechanical stimulation, has been speculated to be an etiologic factor for this marginal bone resorption. It appears that when the implant heads have been placed at the crest of the alveolar bone cortical bone will change in the process of establishing a biologic width, and that this modeling/ remodeling behavior typically occurs to the level where the screw threads start and/ or the roughened surface topography begins. Implant design should therefore take into consideration the bone remodeling in establishingthe biological width. The use of a roughened crest module that is level with the crest of the bone may providea positive stress stimulus to the bone and decrease bone loss in this area, while the smooth part of the crestal module, above the level of crestal bone, should provide an area for connective and epithelial tissue contact. (Adapted from a review article from U Michigan Dr. Wang)
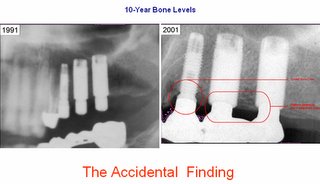
Implant neck (crest module) :The highest bone stresses have been reported to be concentrated in the cortical bone in the region of the implant neck as demonstrated in Finite Element Analysis (FEA) of loaded implants with or without superstructure. This is consistent with findings from experimentsand clinical studies that demonstrated that bone loss begins around the implant neck. It has been suggested that the implant neck should be smooth/ polished, supporting the belief that the crest module should not be designed for load bearing. However, significant loss of crestal bone has been reported for implants with 3 mm long smooth polished necks. Following the placement of an endosseous implant,there is an initial bone modeling/ remodeling during healingand the establishment of a biological seal around the neck of the implant. This bone modeling for biologic seal is acombination of a 1.0-1.5 mm junctional epithelium and a 1.5-2.0 mm connective tissue region that is established superior to the alveolar crest. Evidence from in vivo studies supports the observation of establishment of a biologic seal. Hammerle et al did not observe crestal bone to be maintained above the junction of the Titanium Plasma-sprayed Surface (TPS) and machined neck with ITI implant system,and they concluded that polished implant collars do not integrate, as Buser et al demonstrated in his mini-pigmodel. Similarly, bone modeling occurs to the level where the porous surface begins, with the Endopore implants. Disuse atrophy, due to sub-normal mechanical stimulation, has been speculated to be an etiologic factor for this marginal bone resorption. It appears that when the implant heads have been placed at the crest of the alveolar bone cortical bone will change in the process of establishing a biologic width, and that this modeling/ remodeling behavior typically occurs to the level where the screw threads start and/ or the roughened surface topography begins. Implant design should therefore take into consideration the bone remodeling in establishingthe biological width. The use of a roughened crest module that is level with the crest of the bone may providea positive stress stimulus to the bone and decrease bone loss in this area, while the smooth part of the crestal module, above the level of crestal bone, should provide an area for connective and epithelial tissue contact. (Adapted from a review article from U Michigan Dr. Wang)The concept was found accidentally !


The Only Way To Provide For Your Patients Is To Adapt.
With the increasing demands for implant therapy, the Provide™ Restorative System offers both surgical and restorative clinicians more options and greater flexibilityto meet these demands and better serve patients. Provide Abutments give implant surgeons four collar height options for unmatched surgical flexibility. In addition, because the implant is placed at bone level and not transgingivally, the final crown margin is not pre-determined at the time of surgery and there is no need to prepare the implant if or when the tissue recedes. 
Certain™QuickSeat™Connection
Snap-Fit Impression Components
Superior Surgical And Restorative Flexibility
Surgical Flexibility
1.No Need To Determine Final Crown MarginAt The Time Of Surgery
2.Multiple Collar Heights (1, 2, 3 and 4mm)
3. No Need To Prepare Implant Due To Tissue Recession
4.Use In A One- Or Two-Stage Surgical Protocol
5.Opportunity To Platform Switch To Preserve Crestal Bone
6.Ability To Change Abutment At A Later Date

 The Prevailing Biologic Width Hypothesis:
The Prevailing Biologic Width Hypothesis: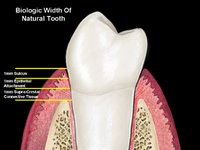

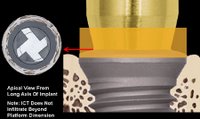
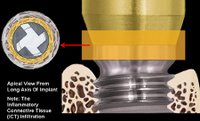

>>>Another system for "Paltform Switch" concept: Astra
The system is based on three core features: Conical Seal Design™ abutment connection, the original MicroThread™ implant neck and the unique OsseoSpeed™ surface 





0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home