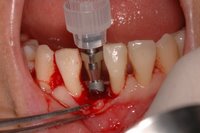
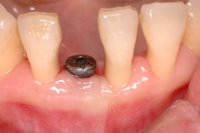
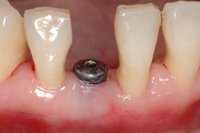
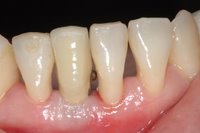
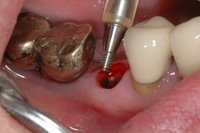
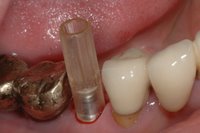
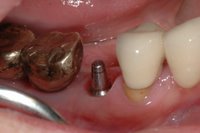
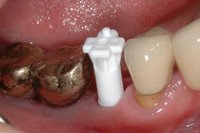
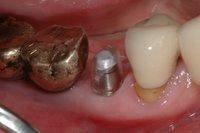
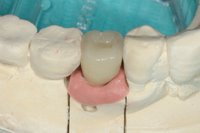
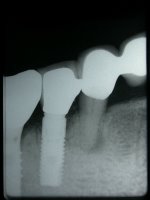
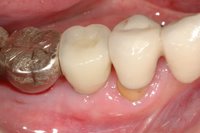
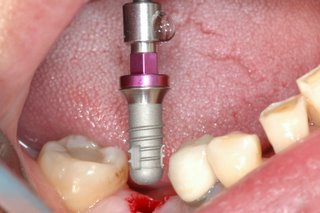
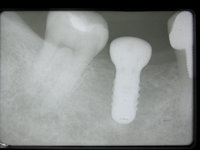
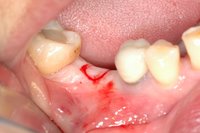
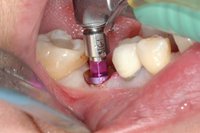
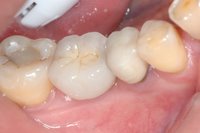
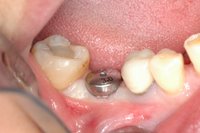
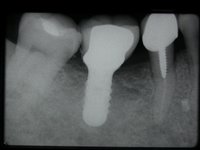
Sky-Implant-System

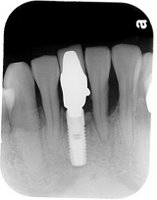
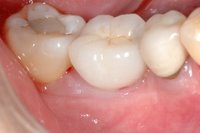
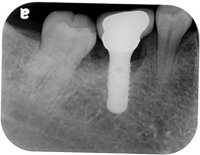
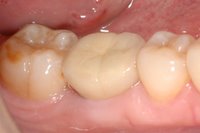
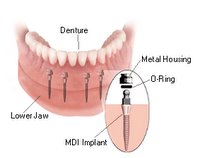
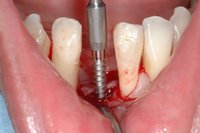
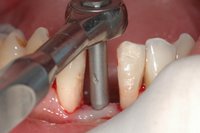
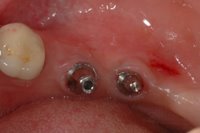
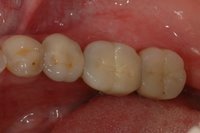
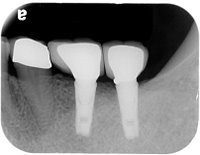
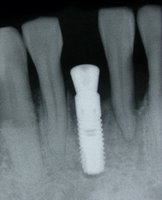
An implant system which fulfills all essential requirements on modern dental implantology in a perfect way. Treatment time and costs can be reducedconsiderably thanks to the simple system concept and the maximum reliability. The Sky-Implant system was developed by practitioners and has been used by experienced implantologists and beginners for two years. More than 15,000 Sky implants have been successfully integrated since 2002. The advantages of the Sky-Implant system at a glance -Optimization of the primary stability-One abutment diameter for all implant diameters-Reduction of the implant accessories-Torx as inner connection-Simpler preparation of the implant bed with the SIS drill set-Funnel-shaped depression at the inner connection-Rounded implant apex-Transfer axis = transfer abutment-Gingiva former = bar segment -Titanium grade 4 kv (cold formed)-Modular system
Product Survey (pdf)
Presentation of the system (pdf)
article: The implant as a tap (pdf)
article: The special benefits of the SKY-Implant system from the prosthetic view (pdf)
article: Immediate loading of implants (pdf)
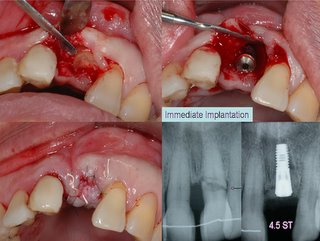
article: immediate implantation and immediate loading (pdf)
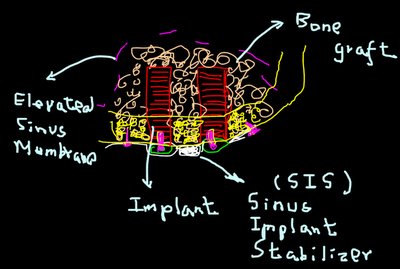
**Sinus Implant Stabilizer (designed by Dr. Manfred Lang; a special lecture in Taiwan)

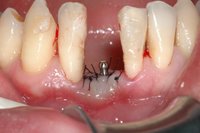
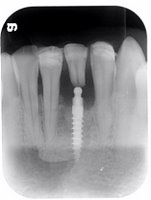
Using the SIS-Sinus Implant Stabilizer one step sinus lift is possible. The implants are stabilized by the SIS and drifting into the sinus is prevented. Additionally the SIS can be fixed with Mondeal microscrews of the ARC System
(A sinus dental implant assembly stabilizer comprising (a) an elongated implant having an internal recess at one end, (b) an insert removably fitting into said recess, and having a head projecting laterally beyond said recess, (c) a washer capable of being removably held in fixed position by said implant and insert, and (d) a nut having an opening to fit over said implant of a size and internal configuration so as to be held in position on said implant, said nut holding said nut securely when said implant is being inserted into said nut.)
ARCS System: The Mondeal Alveolar Crest Reconstruction System; ARCS has been designed and developed to meet with the requirements of modern dental implantology.
Vol. 2 No. 2 Pos. 42
Development and properties of resorbable implant stabilizer concerning sinus lift operation
Author(s): Alfred Johannes Patyk1*, Alberto Nadalini2, Oliver Duesmann3, Hans-Albert Merten41Dept. of Prosthetic Dentistry I3Dept. Orthodontics4Dept. of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Goettingen2Dentist, Trento, Italia
Abstract: To obtain a sufficient primary stability of implants in the lateral maxillary area, a bone thickness of minimum 4 mm is necessary, but often additional osteoplastic operations are required. Regarding this, several sinus lift techniques are known. In this case, the use of an implant stabilizer made of resorbable synthetic material reduces the operation invasivity. For this purpose, a polylactate implant stabilizer with appropiate shape and function has been developed. The following material’s characteristics, such as the material’s hydrolysis, the reduction of the molecular weight and the mechanical retention on the implant have been analysed in vitro. Hydrolysis has been performed following ISO/TC 150 SC 1 standard, and its effects have been documented by SEM images and illustrated with degradation curves. The mechanical properties are defined by the stabilizer’s traction forces in the direction of the implant shaft. Before hydrolysis, the median traction force is 118 [N], one month after, it is reduced to 94 [N] and three months after hydrolysis, the complete absence of any retention force is achieved. The stabilizer has been inserted in the subperiostal tissue of a Goettingen mini pig‘s frontal bone. Four months later, the material has been removed. The presented histological preparation shows the osteo-inductive properties of the stabilizer.
@ASIS-The Autologous Sinus Implant Stabilizer
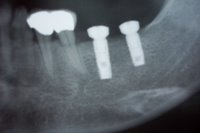
In cases of sinus lifts with an extremely low height of residual local bone the primary stability of the implants is achieved through a cortico-cancellous bone block graft (ASIS) from the mandibular angle instead of a manufactured splint (SIS ®). This produces both vertical and/or lateral augmentation of atrophied alveolar process at the same time






 surface.
surface.